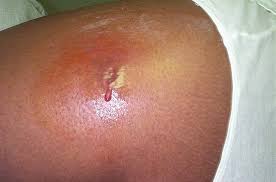
A boil is a skin infection that starts in a hair follicle or oil gland. Also referred to as a skin abscess, it is a localised infection deep in the skin. A boil generally starts as a reddened, tender area. Over time, the area becomes firm and hard.Â
Eventually, the center of the abscess softens and becomes filled with infection-fighting white blood cells that the body sends via the bloodstream to eradicate the infection. This collection of white blood cells, bacteria, and proteins is known as pus. Finally, the pus “forms a head,†which can be surgically opened or spontaneously drain out through the surface of the skin.
What Causes Boils?
There are many causes of boils. Boils are usually caused by a type of bacteria called Staphylococcus (staph). Many staph infections develop into abscesses and can become serious very quickly. This germ can be present on normal skin and enters the body through tiny breaks in the skin or by traveling down a hair to the follicle.
Some boils can be caused by an ingrown hair. Others can form as the result of a splinter or other foreign material that has become lodged in the skin that causes the infection to develop.
Are Boils Contagious?
Boils themselves are not contagious, but the bacteria that cause boils are. Until it drains and heals, an active skin boil is contagious. The infection can spread to other parts of the person’s body or to other people through skin-to-skin contact or the sharing of personal items.
What Is the Treatment for a Boil?
Most simple boils can be treated at home. Ideally, the treatment should begin as soon as a boil is noticed since early treatment may prevent later complications. The primary treatment for most boils is heat application, usually with hot soaks or hot packs.
Heat application increases the circulation to the area and allows the body to better fight off the infection by bringing antibodies and white blood cells to the site of infection. Do not pop the boil with a needle. This usually results in making the infection worse.
Should Boils Be Drained?
As long as the boil is small and firm, opening the area and draining the boil is not helpful, even if the area is painful. However, once the boil becomes soft or “forms a head†(that is, a small pustule is noted in the boil), it can be ready to drain. Once drained, pain relief can be dramatic.
Most small boils, such as those that form around hairs, drain on their own with soaking and/or heat application. On occasion, and especially with larger boils, the larger boil will need to be drained or “lanced†by a health-care practitioner. Frequently, these larger boils contain several pockets of pus that must be opened and drained.
Should Boils Be Treated With Antibiotics?
Antibiotics are often used to eliminate the accompanying bacterial infection. Especially if there is an infection of the surrounding skin, the doctor often prescribes antibiotics. However, antibiotics are not needed in every situation. In fact, antibiotics have difficulty penetrating the outer wall of an abscess and often will not cure an abscess without additional surgical drainage. In most cases, incising and draining the boil is sufficient to cure the infection.
When Should I Seek Medical Attention?
You should call your doctor and seek medical attention if: the boil is located on your face, near your spine, or near your anus; a boil is getting larger; the pain is severe; you have a fever; the skin around the boil turns red or red streaks appear; you have a heart murmur, diabetes, any problem with your immune system, or use immune-suppressing drugs (for example, corticosteroids or chemotherapy) and you develop a boil; the boil has not improved after five to seven days of home treatment; you get many boils over several months.
What Can Be Done to Prevent Boils (Abscesses)?
Good hygiene and the regular use of antibacterial soaps can help to prevent bacteria from building up on the skin. This can reduce the chance for hair follicles to become infected and prevent the formation of boils. Your health-care practitioner may recommend special cleansers such as Hibiclens to further reduce the bacteria on the skin.